C Program Output: Secant Method. Enter initial guesses: 1 2 Enter tolerable error: 0.00001 Enter maximum iteration: 10 Step x0 x1 x2 f (x2) 1 1.000000 2.000000 2.200000 1.248001 2 2.000000 2.200000 2.088968 -0.062124 3 2.200000 2.088968 2.094233 -0.003554 4 2.088968 2.094233 2.094553 0.000012 5 2.094233 2.094553 2.094552 0.000001 Root is: 2.094552. If you change that od: to od; then it won't suppress the display of output from the statements within the loop. Install miracast driver windows 10. Office 2019 windows 7 pro. Doing so would reveal details of what your code is doing. The main problem is that the code within the loop doesn't make use of ind. It is hard-coded to assign to x2 and make use of x1 and x0.
To find the value of x or roots of the equation, we may apply the Secant method. In this method, the derivative may be approximated by a backward finite divided difference approach. So, the function may be expressed as,
This method is convenient when evaluating derivative for some function is difficult in Newton-Raphson method. Now, the above equation may be substituted in Newton-Raphson’s formula to get the following algorithm.
In contrast to Newton-Raphson method, two initial assumptions are made for the two unknowns’ xi-1 and xi.
For the proper initial guess for x, graphical method is applied to visualize the characteristics of the function. The MATLAB commands generate the plot of the function f(x). This function is plotted with respect to the values of x from -10 to +10. The following figure shows the function plot. From the plot, the function changes sign when x is between 2 to 3. So, the root lies in this interval. And, in the program developed for Secant method, two initial guesses for xi-1 and xi are 2 and 3 respectively.
However, more close observation reveals two roots, which are shown in the following figure. In this time, the range of x is decreased significantly for precise investigation between -2 to +2 as this interval seems unclear in the previous figure for the presence of any roots.
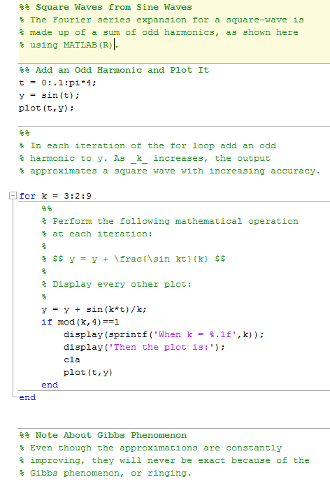
C Program For Secant Method With Output Number
C Program For Secant Method With Output
So, the above figure shows the existence of other two roots, which lie in between 0.1 to 1 and at the origin. The origin is obvious for this case, and there is no need for any further estimation by numerical methods. But, for the interval 0.1 to 1, the accurate and precise approximation is necessary. For this, the two initial guesses are set to 0.1 and 1 for xi-1 and xi accordingly.
The following Secant formula is implemented to approximate the two roots lie in the intervals 2 to 3 and 0.1 to 1. The results are shown after the program.
% Definition of a function 'secant' to solve equation by Secant Method
function [x,ea] = secant(X,X0,etol)
format long;
% Input: X,X0, etol=Tolerance definition for error
% Iterative Calculations
while (1)
% Implementation of Secant Algorithm
solution = X-((exp(X)-(2*X^2)-1)*(X0-X))/((exp(X0)-(2*X0^2)-1)-(exp(X)-(2*X^2)-1));
X0=X;

if (solution-solutionprevious)~=0 % Approximate percent relative error
ea=abs((solution - solutionprevious)/solution)*100;
end
if ea<=etol,
break,
end
% Iterations
2.597424571529533
2.858723109017894
2.842657964680533
2.842673428005184
>> secant(1, 0.1, 1e-5)
C Program For Secant Method With Output Data

0.570046187158243
0.682985699401547
0.742065590882227
0.740850398734311
C Program For Secant Method With Output Function
So, the solutions for the equation are 2.842673428005184, 0.740850398734311 and 0.
C Program For Secant Method With Output Example
#SecantMethod #RootsofEquations #Matlab #NumericalMethod #Blog #Blogger